Ahead-looking: Downscaling has lengthy been the driving drive in technological progress – from boosting computing energy by smaller transistors to advancing show know-how with micro-LEDs. Now, researchers from Zhejiang College and the College of Cambridge are pushing the boundaries of LED innovation even additional, unveiling the world’s smallest LEDs: nano-PeLEDs, based mostly on perovskite semiconductors.
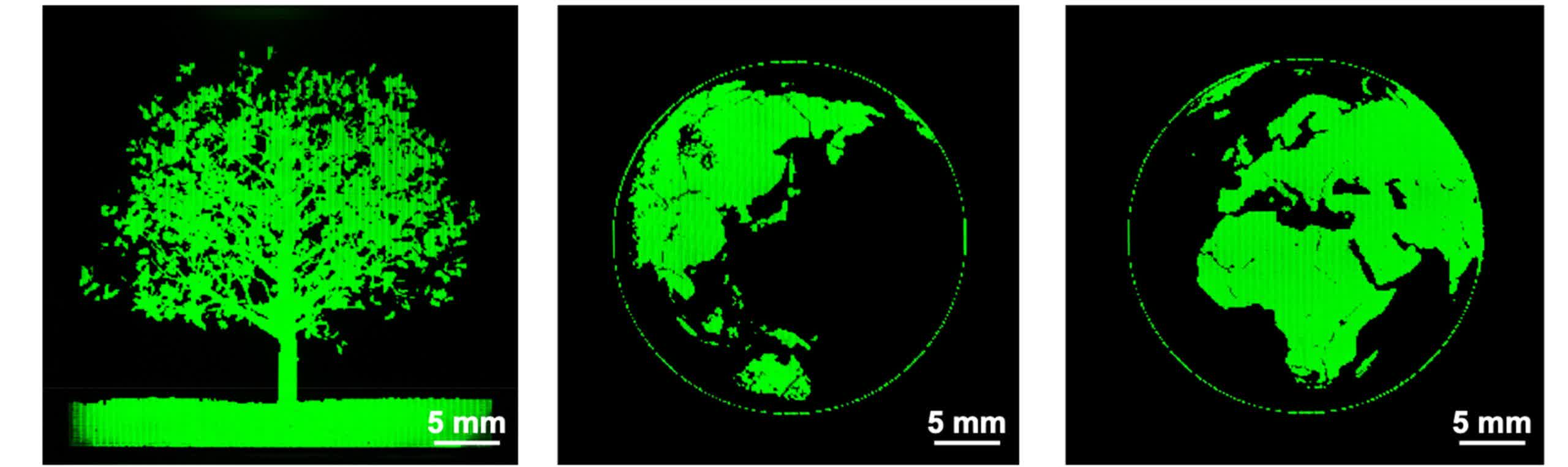
These nano-PeLEDs characteristic pixel lengths as small as 90 nanometers, enabling an unprecedented pixel density of 127,000 pixels per inch (PPI). For comparability, a typical 27-inch 4K gaming monitor has a pixel density of simply 163 PPI.
“Making digital units smaller is an eternal pursuit for scientists and engineers,” stated Professor Di Dawei, Deputy Director of the Worldwide Analysis Middle for Superior Photonics at Zhejiang College.
He defined that whereas micro-LEDs based mostly on III-V semiconductors are thought of state-of-the-art, their effectivity drops sharply when pixel sizes fall under 10 micrometers – a limitation that has hindered their use in ultra-high-resolution shows.
Not like standard micro-LEDs, nano-PeLEDs exhibit minimal efficiency degradation even at microscopic scales. This resilience is attributed to their distinctive composition: halide perovskites – a category of semiconductors extra generally related to photo voltaic cells. “Halide perovskites are a brand new class of semiconductors,” famous Professor Zhao Baodan of Zhejiang College.
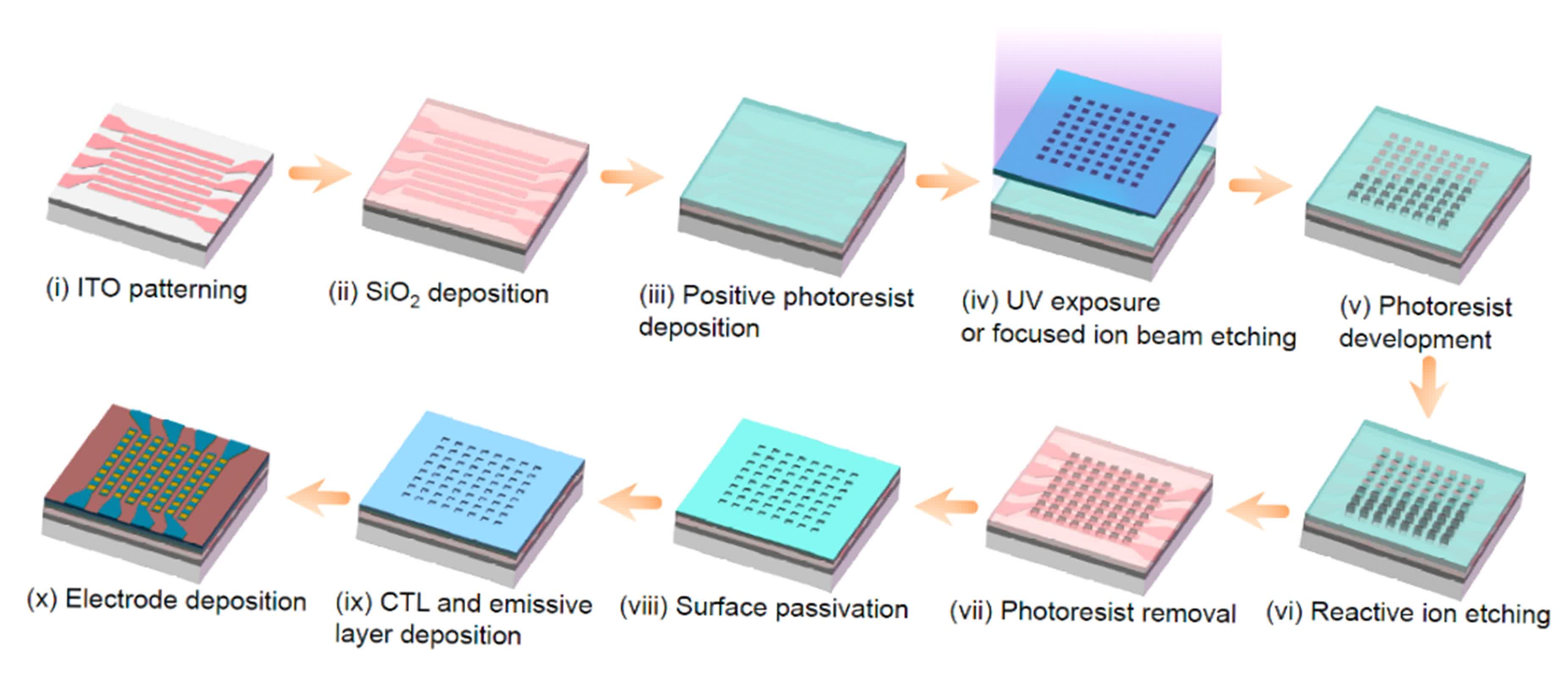
Creating nano-PeLEDs, nonetheless, was no easy process. Perovskite supplies are notoriously fragile and inclined to wreck throughout standard photolithographic processes used to sample LED shows. To beat this, the analysis staff developed a novel fabrication methodology involving lithographically patterned home windows in an insulating layer. This method protects the fragile perovskite materials whereas preserving excessive picture high quality.
“Standard photolithographic processes will not be appropriate for direct patterning of the perovskite layers – it could harm the supplies,” stated Lian Yaxiao, first writer of the examine, printed in Nature. “This downside is overcome by our localized contact fabrication scheme.”
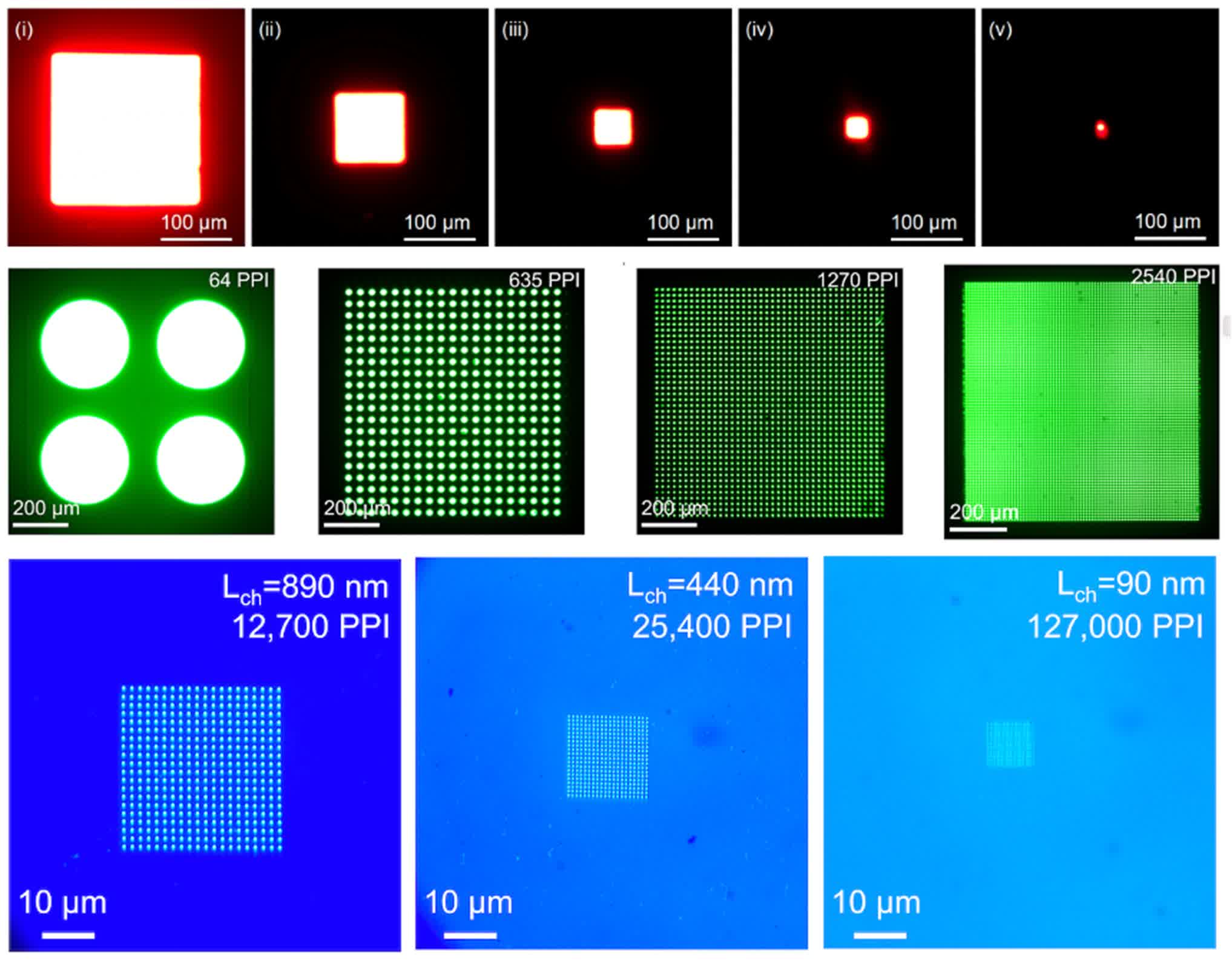
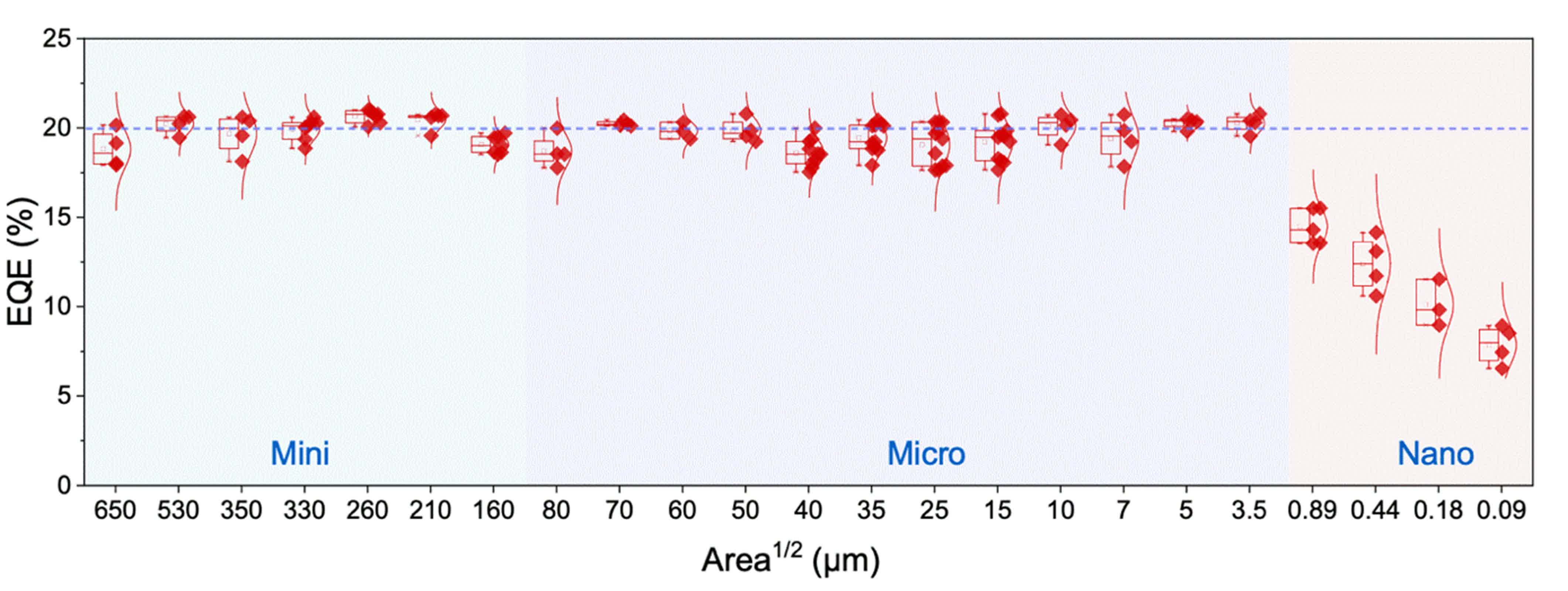
The staff demonstrated that their inexperienced and near-infrared nano-PeLEDs maintained exterior quantum efficiencies of round 20 % throughout pixel sizes starting from a number of hundred microns down to simply 3.5 microns.
Even at excessive miniaturization – roughly 180 nanometers – the drop in effectivity was considerably lower than that seen in conventional micro-LEDs. This means that nano-PeLEDs may outperform III-V semiconductor-based micro-LEDs in purposes requiring ultra-small pixels.
Whereas nano-PeLEDs provide super promise for high-resolution shows, sensible implementation requires integration with programmable circuits able to dynamic content material supply. To that finish, Zhejiang College has partnered with LinkZill, a Hangzhou-based firm specializing in thin-film transistor (TFT) know-how.
Collectively, they developed a prototype active-matrix micro-PeLED show pushed by a TFT backplane. This prototype is essential to commercializing nano-PeLED know-how and unlocking its potential for advanced pictures and video playback.
As researchers proceed refining this know-how, its potential purposes are quickly increasing. The ultra-high decision enabled by nano-PeLEDs may redefine show requirements throughout varied industries – from gaming and augmented actuality to medical imaging.





