Reducing corners: In a stunning flip for the fast-evolving world of synthetic intelligence, a brand new examine has discovered that AI-powered coding assistants may very well hinder productiveness amongst seasoned software program builders, quite than accelerating it, which is the principle cause devs use these instruments.
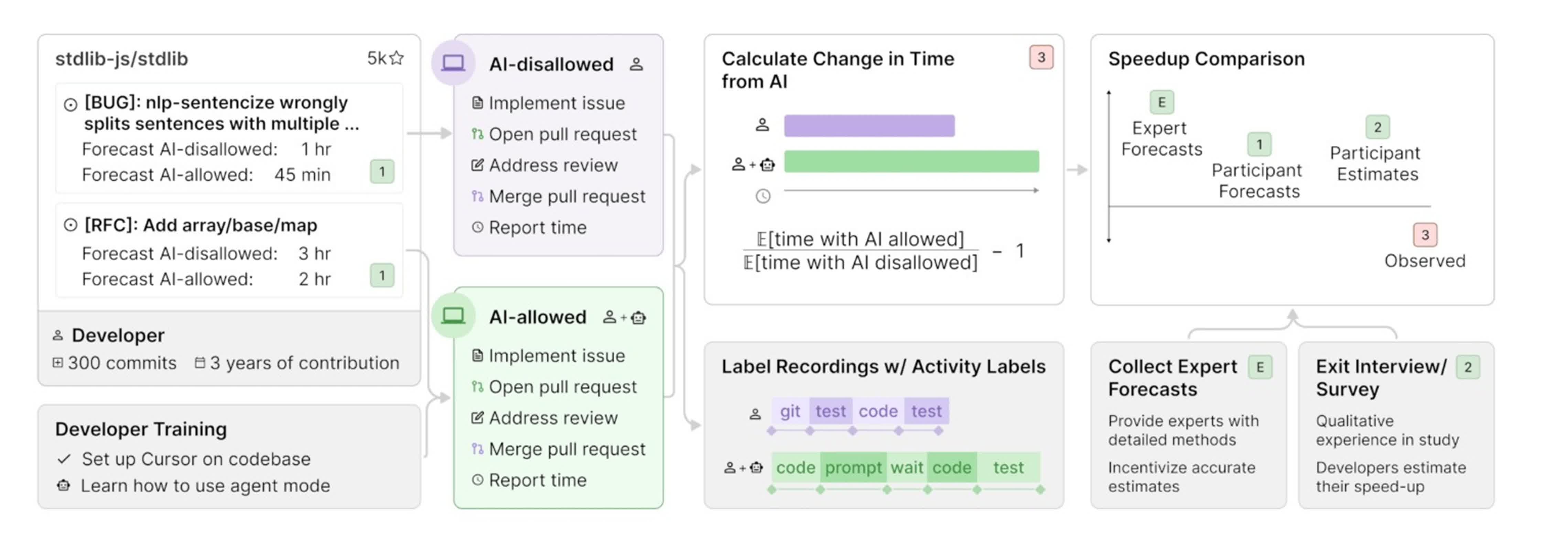
The analysis, carried out by the non-profit Mannequin Analysis & Menace Analysis (METR), got down to measure the real-world affect of superior AI instruments on software program growth. Over a number of months in early 2025, METR noticed 16 skilled open-source builders as they tackled 246 real programming duties – starting from bug fixes to new function implementations – on giant code repositories they knew intimately. Every activity was randomly assigned to both allow or prohibit using AI coding instruments, with most contributors choosing Cursor Professional paired with Claude 3.5 or 3.7 Sonnet when allowed to make use of AI.
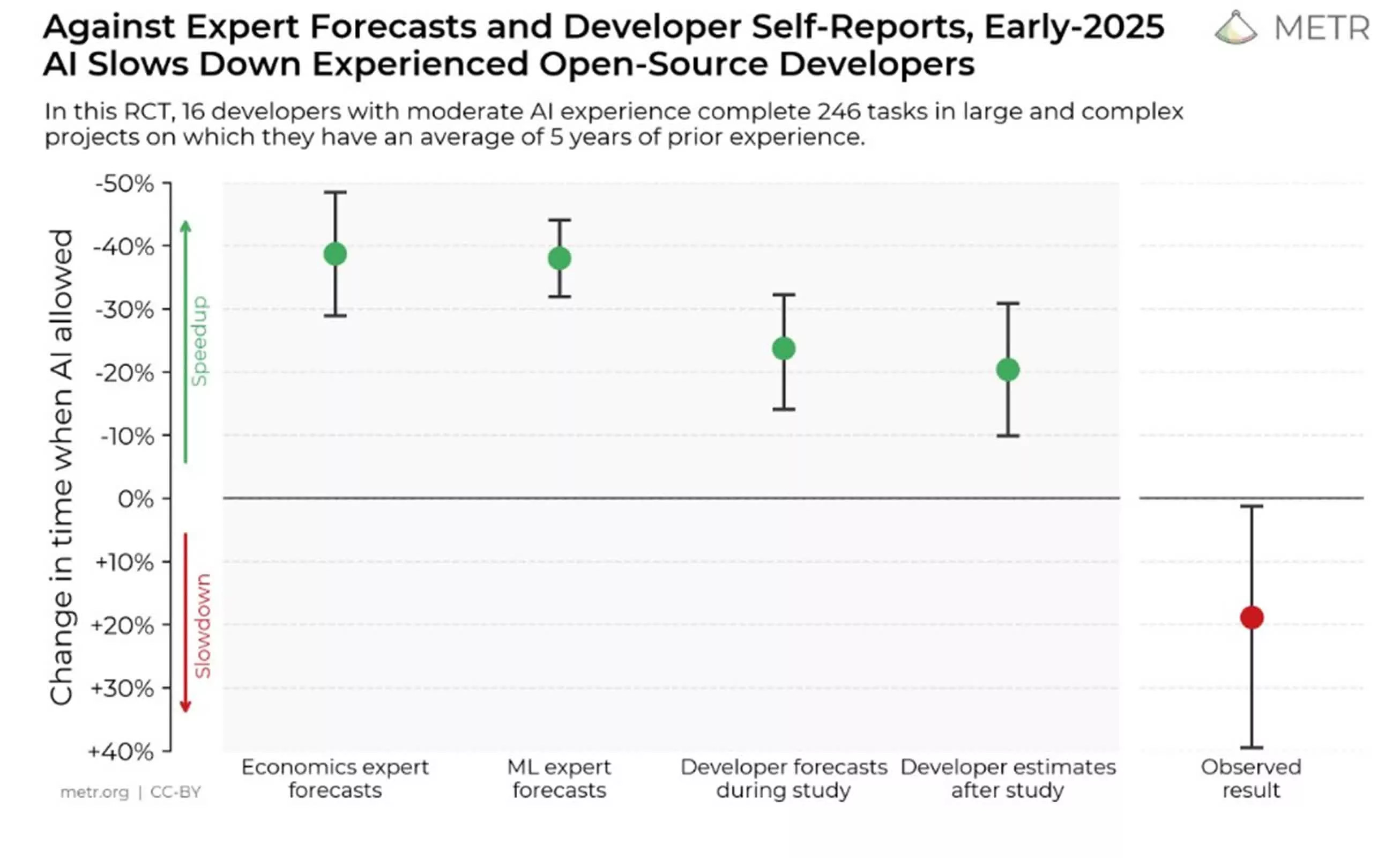
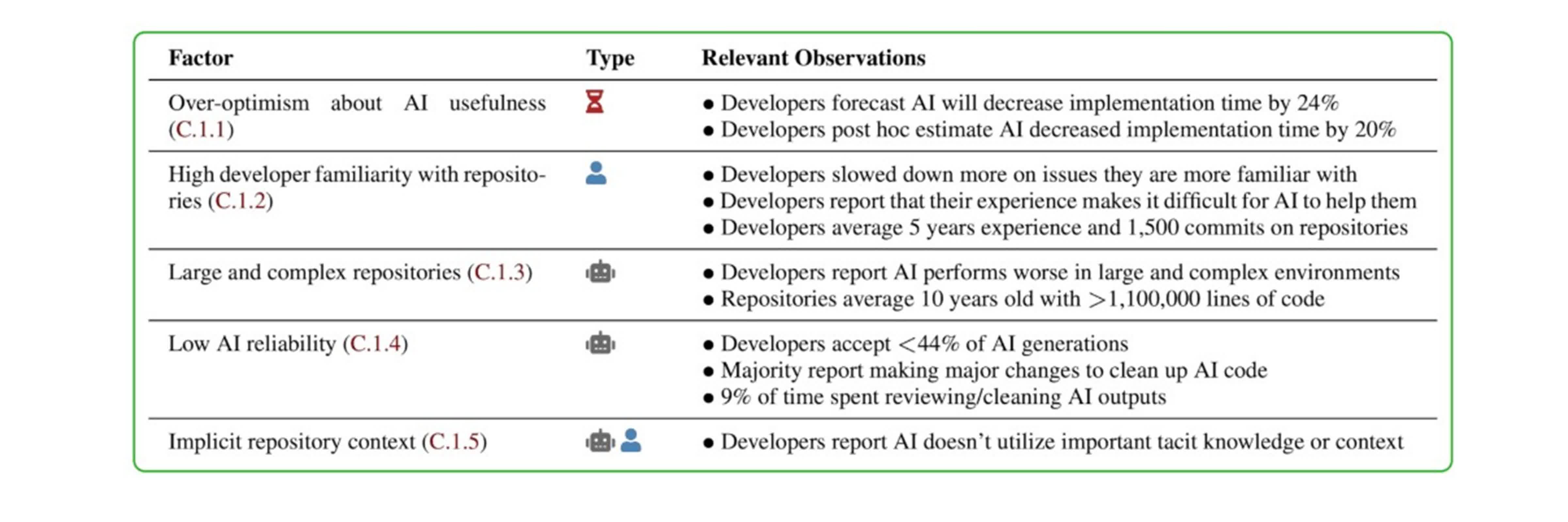
Earlier than starting, builders confidently predicted that AI would make them 24 p.c sooner. Even after the examine concluded, they nonetheless believed their productiveness had improved by 20 p.c when utilizing AI. The truth, nevertheless, was starkly completely different. The info confirmed that builders truly took 19 p.c longer to complete duties when utilizing AI instruments, a end result that ran counter not solely to their perceptions but in addition to the forecasts of consultants in economics and machine studying.
The researchers dug into attainable causes for this sudden slowdown, figuring out a number of contributing components. First, builders’ optimism concerning the usefulness of AI instruments typically outpaced the know-how’s precise capabilities. Many contributors have been extremely acquainted with their codebases, leaving little room for AI to supply significant shortcuts. The complexity and dimension of the tasks – typically exceeding 1,000,000 traces of code – additionally posed a problem for AI, which tends to carry out higher on smaller, extra contained issues. Moreover, the reliability of AI solutions was inconsistent; builders accepted lower than 44 p.c of the code it generated, spending important time reviewing and correcting these outputs. Lastly, AI instruments struggled to understand the implicit context inside giant repositories, resulting in misunderstandings and irrelevant solutions.
The examine’s methodology was rigorous. Every developer estimated how lengthy a activity would take with and with out AI, then labored by means of the problems whereas recording their screens and self-reporting the time spent. Contributors have been compensated $150 per hour to make sure skilled dedication to the method. The outcomes remained constant throughout varied consequence measures and analyses, with no proof that experimental artifacts or bias influenced the findings.
Researchers warning that these outcomes shouldn’t be overgeneralized. The examine targeted on extremely expert builders engaged on acquainted, advanced codebases. AI instruments should provide better advantages to much less skilled programmers or these engaged on unfamiliar or smaller tasks. The authors additionally acknowledge that AI know-how is evolving quickly, and future iterations might yield completely different outcomes.
Regardless of the slowdown, many contributors and researchers proceed to make use of AI coding instruments. They be aware that, whereas AI might not all the time pace up the method, it may make sure points of growth much less mentally taxing, remodeling coding right into a activity that’s extra iterative and fewer daunting.